The Comprehensive 1st Guide to Utilities: Types, Importance, and Future Trends
Utilities are an essential part of modern life, yet they often go unnoticed until they are disrupted. From electricity to water, gas, and digital services, utilities form the backbone of residential, commercial, and industrial operations. In this article, we explore the concept of utilities, their types, importance, management, technological advancements, and the future of utility services worldwide.
1. Understanding Utilities
The term utilities refers to the essential services required to support daily life and economic activity. These services ensure comfort, safety, and efficiency in homes, businesses, and public infrastructure. Utilities are typically provided by public or private entities and include both traditional and modern services such as electricity, water, natural gas, sewage, and telecommunications.
Utilities are critical because they enable societies to function smoothly. Without reliable utilities, communities face challenges such as health risks, economic setbacks, and reduced quality of life. For businesses, utility management impacts operational efficiency, costs, and sustainability.
2. Types of Utilities
Utilities can be broadly categorized into several types:
2.1 Electricity
Electricity is one of the most fundamental utilities. It powers homes, businesses, healthcare facilities, and industries. Reliable electricity is vital for lighting, appliances, machinery, and digital technologies. The electricity sector is increasingly incorporating renewable sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, aiming for sustainable energy solutions.
2.2 Water Supply
Access to clean water is crucial for health, sanitation, and agriculture. Utilities provide water distribution networks, treatment plants, and water quality monitoring. Water utilities ensure that households and businesses receive potable water while also managing wastewater treatment to protect the environment.
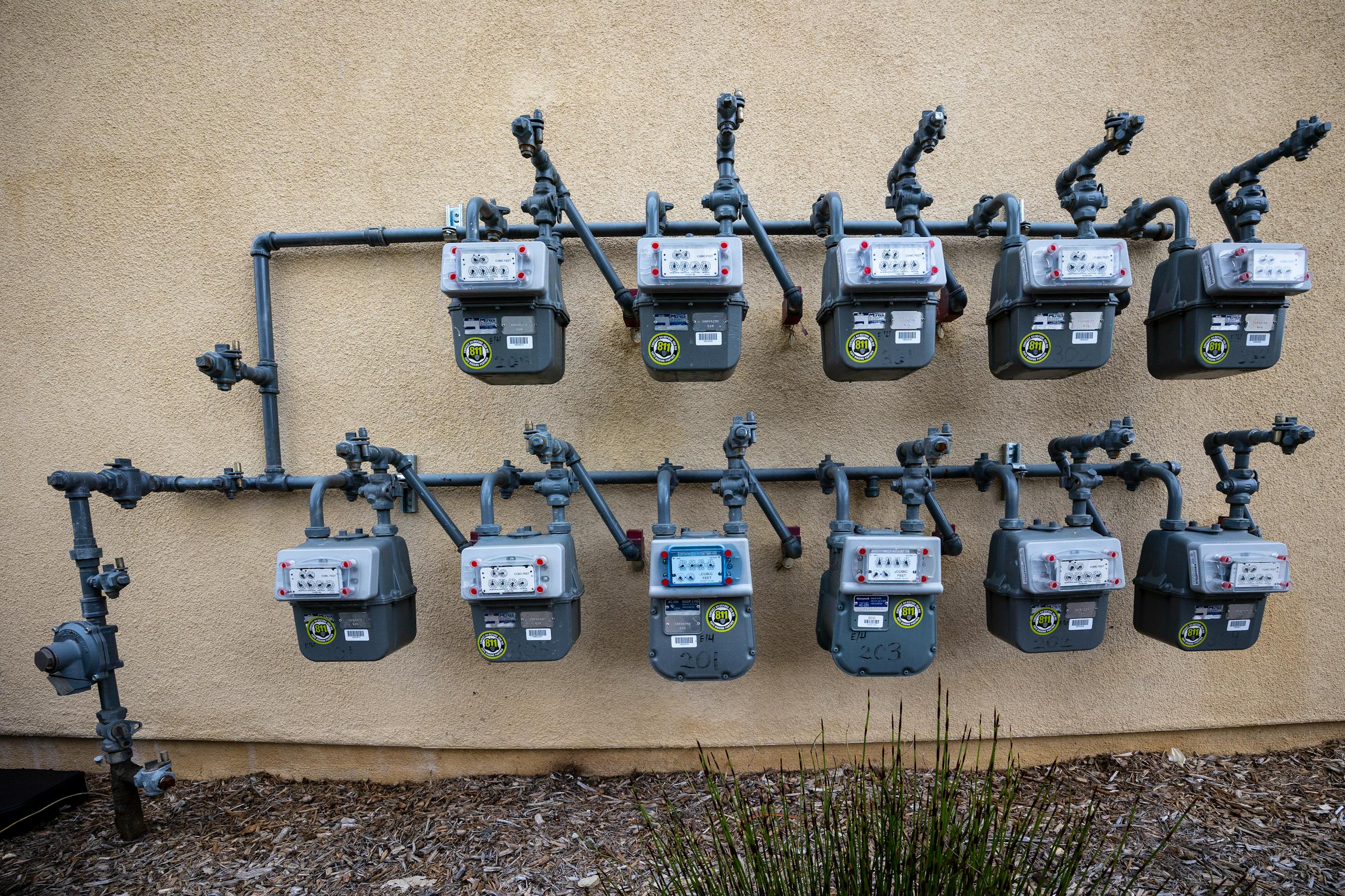
2.3 Natural Gas
Natural gas is widely used for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. Gas utilities manage extraction, transportation, and distribution. Modern gas utilities focus on safety, efficiency, and reducing carbon emissions through cleaner energy alternatives.
2.4 Waste Management and Sewage
Waste management and sewage utilities play a significant role in public health and environmental protection. Proper treatment of waste and sewage prevents disease outbreaks and pollution. These utilities include garbage collection, recycling, wastewater treatment, and sewage disposal systems.
2.5 Telecommunications and Internet Services
Digital utilities, such as internet and telecommunication services, have become essential in the 21st century. They enable communication, education, business operations, and access to digital resources. Utilities in this category include broadband networks, mobile services, and cloud computing infrastructure.
3. Importance of Utilities in Daily Life
Utilities are integral to modern life, impacting health, productivity, and economic growth. Their importance can be highlighted in several ways:
3.1 Health and Hygiene
Water, sanitation, and waste management utilities ensure clean living conditions. They prevent waterborne diseases, contamination, and environmental hazards. Reliable utilities improve overall public health and life expectancy.
3.2 Economic Development
Industries, businesses, and service sectors rely on electricity, gas, and digital connectivity. Disruptions in utility services can lead to production downtime, financial losses, and reduced competitiveness. Efficient utilities are crucial for economic stability and growth.
3.3 Comfort and Quality of Life
Utilities enhance comfort by providing heating, cooling, lighting, and communication services. They are essential for modern lifestyles, enabling convenience and efficiency in households.
3.4 Environmental Sustainability
Sustainable utility practices, such as renewable energy use and wastewater recycling, reduce environmental impact. Utilities play a key role in addressing climate change and conserving natural resources.
4. Utility Management and Efficiency
Managing Utilitie effectively is critical for reducing costs, improving reliability, and promoting sustainability. Both public and private utility providers employ various strategies to enhance utility management:
4.1 Smart Metering
Smart meters allow real-time monitoring of electricity, water, and gas consumption. They help consumers track usage, identify inefficiencies, and reduce wastage.
4.2 Energy Management Systems
Energy management systems optimize electricity and gas usage in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. These systems reduce operational costs and carbon emissions.
4.3 Water Conservation Techniques
Utilitie encourage water conservation through leak detection, recycling, and efficient irrigation systems. Advanced monitoring technologies help track water usage and detect anomalies.
4.4 Waste Reduction Programs
Modern Utilitie implement recycling, composting, and proper waste segregation programs. Digital tools and community initiatives enhance waste management efficiency.
5. Technological Advancements in Utilitie
Technology has transformed utility services worldwide, improving efficiency, reliability, and sustainability.
5.1 Renewable Energy Integration
Utilitie are increasingly incorporating renewable energy sources to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and biomass power contribute to cleaner and more sustainable electricity generation.
5.2 Smart Grids and IoT
Smart grids leverage IoT (Internet of Things) technology to monitor and control electricity distribution. They improve grid stability, reduce outages, and allow consumers to manage energy use more effectively.
5.3 Advanced Water Treatment
Water Utilitie utilize advanced filtration, desalination, and monitoring systems to ensure safe drinking water. AI-driven systems optimize water quality and distribution.
5.4 Digital Platforms for Utility Management
Mobile apps and online portals allow consumers to pay bills, track usage, and report issues efficiently. These platforms improve communication between Utilitie and customers.
6. Challenges Facing Utilities
Despite technological advancements, utilities face several challenges:
6.1 Aging Infrastructure
Many regions rely on outdated infrastructure, leading to inefficiencies, leaks, and service disruptions. Upgrading infrastructure requires significant investment.
6.2 Climate Change and Natural Disasters
Extreme weather events impact electricity, water, and waste management services. Utilities must develop resilient systems to withstand floods, storms, and heatwaves.
6.3 Increasing Demand
Urbanization, population growth, and industrial expansion increase the demand for utilities. Providers must scale operations while maintaining reliability and sustainability.
6.4 Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Utilities must adhere to strict regulations on emissions, waste management, and public safety. Compliance requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation.
7. The Future of Utilities
The utility sector is evolving rapidly, driven by technology, sustainability, and changing consumer expectations. Here are some key trends shaping the future:
7.1 Green and Sustainable Utilities
Renewable energy, water recycling, and eco-friendly waste management will become standard. Consumers increasingly demand environmentally responsible utility services.
7.2 Decentralized Utility Systems
Microgrids, localized water systems, and community energy solutions enable more resilient and independent utility services.
7.3 Digital Transformation
AI, IoT, and blockchain technologies will enhance efficiency, transparency, and customer engagement in utilities. Predictive maintenance and smart billing systems will become more prevalent.
7.4 Consumer Empowerment
Consumers will have greater control over their utility usage through smart devices and data-driven insights. Personalized services will improve satisfaction and reduce waste.

8. Conclusion
Utilitie are the backbone of modern life, supporting health, economic activity, and comfort. From electricity and water to digital services and waste management, they ensure societies function efficiently and sustainably. Managing Utilitie effectively, leveraging technology, and embracing sustainable practices are critical for meeting growing demand and addressing environmental challenges.
As we move forward, Utilitie will continue to evolve, integrating smart systems, renewable energy, and consumer-centric approaches. Understanding the importance of Utilitie, investing in their management, and adopting innovative solutions are key to a sustainable and efficient future.
Understanding Utilitie: Essential Services for Modern Life
Utilitie are the backbone of modern society, providing the essential services that enable homes, businesses, and industries to function smoothly. From electricity and water to natural gas and telecommunications, Utilitie are critical for health, comfort, and economic growth. Despite their importance, they often go unnoticed—until a disruption occurs.
Types of Utilitie
The most common types of Utilitie include:
- Electricity: Powers homes, offices, industries, and public infrastructure. With renewable energy sources like solar and wind becoming more prevalent, electricity Utilitie are increasingly focused on sustainability.
- Water Supply: Ensures access to clean drinking water and proper sanitation. Utilitie manage water treatment, distribution, and wastewater management, which are crucial for public health.
- Natural Gas: Used for heating, cooking, and industrial processes. Gas Utilitie focus on safe delivery, efficiency, and reducing environmental impact.
- Telecommunications: Includes internet and mobile services, which have become essential in a digital world. Reliable connectivity enables communication, business operations, and education.
- Waste Management: Covers garbage collection, recycling, and sewage treatment, helping maintain hygiene and protect the environment.
Importance of Utilitie
Utilitie are vital for everyday life. They support health and hygiene, ensure safety, and improve overall quality of life. For businesses, efficient Utilitie reduce operational costs, enhance productivity, and foster economic growth. Furthermore, sustainable utility practices contribute to environmental protection, helping societies address climate change and resource scarcity.
Managing Utilitie Effectively
Effective utility management ensures reliability and efficiency. Tools like smart meters, energy management systems, and water monitoring technologies allow consumers and providers to track usage, reduce waste, and optimize performance. Modern digital platforms also make it easier to pay bills, report issues, and access real-time data.
The Future of Utilitie
The utility sector is evolving with technology and sustainability in focus. Renewable energy, smart grids, and AI-driven monitoring are transforming traditional utility services. As consumer expectations grow, Utilitie are becoming more efficient, environmentally friendly, and customer-centric, ensuring reliable services for a growing population.
Conclusion: Utilitie are indispensable services that form the foundation of modern living. By understanding their types, significance, and management strategies, individuals and businesses can use Utilitie more efficiently while contributing to a sustainable future.
Utilities are the backbone of modern society, providing the essential services that enable homes, businesses, and industries to function smoothly. From electricity and water to natural gas and telecommunications, utilities are critical for health, comfort, and economic growth. Despite their importance, they often go unnoticed—until a disruption occurs.





